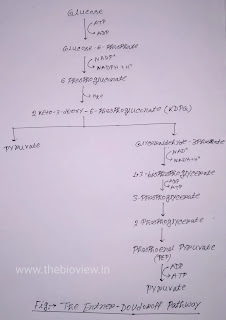
ED pathway or Entner Doudoroff Pathway describes an alternative series of reactions that catabolise Glucose to Pyruvate using a set of enzymes different from those used in either glycolytic of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway. The ED pathway was first reported by Mitchell Doudoroff and Nathan Entner. After their discovery this cycle was given tha name ED pathway.
There are several bacteria that use the ED pathway for matabolism of Glucose and are unable to catalysis the the glycose via glycolytic pathway. For example Pseudomonad sp lacks PFK (Phosphofructokinase), the essential glycolytic enzyme.
Genera in which the ED Pathway is prominent includes gram negetive and gram positive bacteria such as Enterococcus fecalis , Pseudomonas sp , Rhizobium sp , Azotobactor sp.
Entner Doudoroff Pathway (ED Pathway)
Step 1 : Phosphorylation of Glucose
In this step Glucose is converted to Glucose-6-phosphate by enzyme Hexokinase. ATP is required as phosphate group donor and Mg2+ acts as cofactor.
Step 2 : Dehydrogenation
In this step Glucose-6-phosphate is oxidised and converted into 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone by the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This enzyme requires NADP+ as a cofactor.
Step 3 : Hydration
In the third step of ED pathway 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone is converted to 6-phosphogluconate by the enzyme 6-phosphogluconolactonase which requires Ca2+ and Mg2+ as cofactor.
Step 4 : Dehydration
In this step 6-phosphogluconate is dehydrated by the enzyme 6-phosphogluconodehydratase and converted into KDPG ( 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate).
Step 5 : Splitting of KDPG
In the fifth step KDPG is cleaved into Pyruvate and Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate by the enzyme KDPG Aldolase.
Step 6 : Oxidation and Phosphorylation of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
In this step Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase converts Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. NAD+ acts as cofactor in this step of ED Pathway. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidised by releasing high energy electrons, the electrons are picked up by NAD+ and NADH + H+ is formed.
Step : 7 Dephosphorylation of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
In this step the enzyme Phosphoglycerate Kinase catalyses the transfer of phosphate group from 1,3-bisphoglycerate to ADP to form ATP and 3-phosphoglycerate is produced as a product.
Step 8 : Isomerisation of 3-Phosphoglycerate
In this step the the Phosphate group of 3-phosphoglycerate moves from the third carbon to second carbon by producing 2-Phosphoglycerate. This step is catalysed by the enzyme Phosphoglycerate mutase.
Step : 9 Dehydration of 2-Phosphoglycerate
Enolase catalyses this step, 2-phosphoglycerate is converted to Phosphoenol Pyruvate (PEP). Water is released in this step.
Step 10 : Dephosphorylation of PEP
This is the last step. Phosphate group is transferred from PEP to ADP and as a product ATP and Pyruvate are formed. The reaction is catalysed by Pyruvate Kinase and MG2+ acts as cofactor.
The sequence leading from Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to Pyruvate is catalysed by enzymes common to the Glycolysis or EMP Pathway.
Product calculation in ED pathway
Total ATP formation during ED Pathway = +1
Total NADH formation during ED Pathway = +1
Total NADPH formation = +1
Total H2O formation = +1