What is glycolysis?
The sequence of reactions or pathways in which glucose is degraded anaerobically to form pyruvic acid is called glycolysis. Glycolysis was discovered by three German scientists Embden, Meyerhof and Paranas so this cycle is also called EMP Pathway.
Glycolysis occurs in cytoplasm of the cell and is an universal pathway in all biological systems.
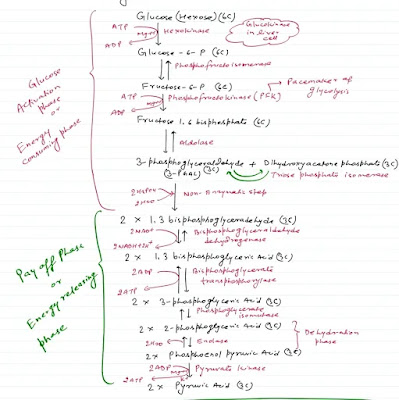 |
| Glycolysis Pathway Diagram |
Glucose + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi —> 2 Pyruvate +2 ATP + 2 NADH + H+ + 2 H20
Phases of Glycolysis
Glycolysis is divided into two phases:
1. Preparatory phase of glycolysis – In preparatory phase breakdown of glucose and low energy phosphorylation occurs and energy is expanded
2. oxidative phase of glycolysis – in oxidative phase the high energy phosphate bonds are formed and energy is released.
10 steps of glycolysis
Step 1 : Phosphorylation
Glucose enters the glycolytic pathway by phosphorylation; the addition of phosphate. Glucose is phosphorylated to Glucose-6-phosphate by ATP in the presence of enzyme Hexokinase or Glucokinase and Mg2+.
Step 2 : Isomerization of Glucose-6-phosphate
Glucose-6-phosphate is changed to its isomer Fructose-6-phosphate with the help of enzyme Phosphohexose isomerase. This is a reversible reaction.
Step 3 : Phosphorylation of Fructose-6-phosphate
Fructose-6-phosphate is further phosphorylated by means of ATP in the presence of enzyme Phosphofructokinase and mg2+ the product is Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
- What is Cot Curve of DNA ? Significance of Cot curve and Cot analysis
- Rhoeo leaf experiment Under Microscope | Study of Representative Plant by Microscopy
Step 4 : Splitting of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
In the step Fructose-1,6-phosphate splits into Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) and Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme Aldolase and Zn2+ acts as cofactor.
Step 5 : Isomerization of DHAP
This is the last step of the preparatory phase. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is used on the direct pathway of Glycolysis but DHAP is not , which can be readily converted into Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. The enzyme involved in this reaction is Triose phosphate isomerase. This is a reversible process.
Phase 6 : Oxidation and Phosphorylation of Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
In the presence of enzyme Glyceraldehyde phosphate Dehydrogenase, Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate loses hydrogen to NAD to form NADH2 and accepts inorganic Phosphate to form 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
Step 7 : Formation of ATP
One of the two phosphate of bisphosphoglycerate is linked by a high energy bond. It can synthesize ATP and form 3-Phosphoglycerate. The enzyme is Phosphoglycerate kinase. The direct synthesis of ATP from metabolites is called Substrate Level Phosphorylation.
Step 8 : Isomerization of 3-Phosphoglycerate
3-Phosphoglycerate is changed to its isomer 2-Phosphoglycerate by enzyme Phosphoglyceromutase, which transfers the phosphate from third to second carbon.
Step 9 : Dehydration of 2-Phosphoglycerate
Enolase catalyses this step. 2-phosphoglycerate is converted to Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). 2-phosphoglycerate loses water from structure and forms a double bond.
Step 10 : Formation of Pyruvic Acid
In the last step of Glycolysis, the Phosphate group is transferred from PEP to ADP and as a product ATP and Pyruvate are formed. This reaction is catalysed by Pyruvate Kinase. Mg2+ acts as cofactor.
Glycolysis Pathway Diagram :
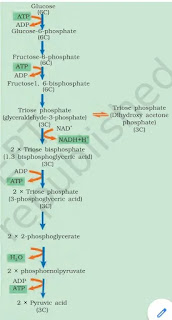 |
| Glycolysis Pathway NCERT |
Net Product of Glycolysis
In glycolysis two molecules of ATP are consumed during double phosphorylation of glucose to form fructose-1, 6 diphosphate. In return four molecules of ATP are produced by substrate level phosphorylation (2 molecules of ATP are produced during each conversion of 1, 3-diphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate and 2 phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate). Since 2 ATP are used, there is a net gain of 2 ATP only.
Net gain of ATP = 4ATP – 2ATP = 2 ATP.
- Two molecules of NADH are formed at the time of oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1, 3-biphosphoglycerate.
- The net reaction is as follows:
Glucose + 2NAD+ + 2ADP+ 2H3PO4 — > 2 Pyruvate + 2NADH + 2H+ + 2ATP
- Each NADH is equivalent to 3 ATP. As a result 6 more ATP molecules are formed. Thus a total of 10 ATP molecules are produced and the total gain of ATP in glycolysis is 8 ATP.
- Intermediates of glycolysis are used for synthesis of important biochemicals. For example, phosphoenolpyruvate yields shikimic acid which is used in synthesis of amino acids, tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine. Tryptophan is raw material for IAA synthesis. The amino acids are employed for synthesis of proteins, alkaloids, flavonoids and lignin. Similarly, pyruvic acid forms amino acid alanine.
How many steps in Glycolysis?
There is total 10 steps in Glycolysis pathway.
Why Glycolysis is called EMP Pathway?
Glycolysis was discovered by three German scientists Embden, Myerhof and Paranas. In their tribute the Glycolysis pathway is also called EMP Pathway.
Where Glycolysis occurs?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cell.
In glycolysis how many ATP are produced?
2 molecules of ATP is produced in Glycolysis. But also additionally 2 NADH molecules also produced.
Which steps are irreversible in Glycolysis?
Out of 10 steps 3 steps are irreversible in Glycolysis pathway. These are 1st , 3rd and last step of Glycolysis.

